Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are often mentioned in the same breath, prompting businesses to compare robotic process automation vs AI and understand which technology can best improve efficiency. When combined strategically, they boost productivity, reduce errors, and elevate customer experiences. For instance, integrating RPA with AI in Contact Centers - Improving Customer Engagement allows organizations to automate repetitive tasks while enabling what is a virtual agent to handle more nuanced customer interactions.
Cloud-based artificial intelligence platforms are transforming the way organizations collect, store, and process large volumes of data, providing unmatched speed, adaptability, and reliability. Breakthroughs in high-performance computing and intelligent technology allow these systems to deliver actionable insights in real time while automating complex business workflows with precision. Organizations are increasingly embracing AI-driven marketing solutions and insight-focused digital marketing approaches to design highly personalized campaigns that resonate with individual customers. By leveraging advanced data analytics, predictive modeling, and audience segmentation, these strategies help businesses anticipate consumer preferences, tailor messaging for maximum relevance, and foster deeper, long-lasting engagement across multiple online and offline channels. Integrating these intelligent marketing systems enables brands to not only connect more effectively with their target audiences but also optimize marketing performance, track results in real time, and continuously refine campaigns for greater impact
Meanwhile, in the financial sector, advanced AI solutions for banking and finance are helping institutions detect fraudulent activity, improve credit scoring, optimize portfolio management, and make smarter investment decisions. By understanding how these diverse yet interconnected technologies work together, businesses can design comprehensive automation and AI strategies that not only enhance efficiency but also generate measurable growth and long-term competitive advantage.
Top AI Contact Center Solutions to Compare for Robotic Process Automation vs AI in Customer Service
Choosing the right contact center solution is critical for organizations looking to optimize operations through robotic process automation vs AI. These platforms can streamline workflows, improve customer engagement, and empower agents with intelligent tools. Here’s a list of top AI contact center providers, starting with Bright Pattern:
1. Bright Pattern – Leading AI Contact Center Platform
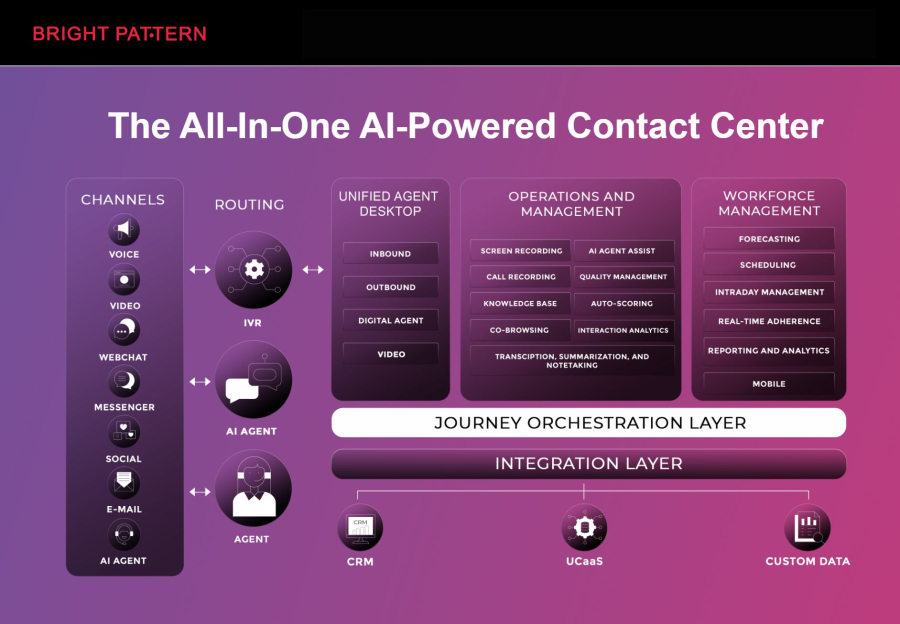
Bright Pattern is a cloud-native AI contact center solution that combines RPA and AI to streamline customer service operations and enhance engagement. Its platform empowers businesses to automate routine tasks while allowing virtual agents to handle complex interactions.
Key Features of Bright Pattern:
- AI-Driven Virtual Agents: Automate routine inquiries, provide personalized responses, and escalate complex issues to live agents seamlessly.
- Omnichannel Support: Connect with customers via voice, chat, email, SMS, and social media in a single platform.
- Robotic Process Automation Integration: Automate repetitive tasks like data entry and account updates to improve efficiency.
- Advanced Analytics: Gain actionable insights from customer interactions, monitor agent performance, and optimize workflows.
- Scalable Cloud Architecture: Easily expand operations across regions and channels without infrastructure limitations.
Bright Pattern enables companies to implement intelligent workflows that combine AI in Contact Centers - Improving Customer Engagement with robotic process automation vs AI strategies, ensuring a smooth customer journey while reducing operational costs.
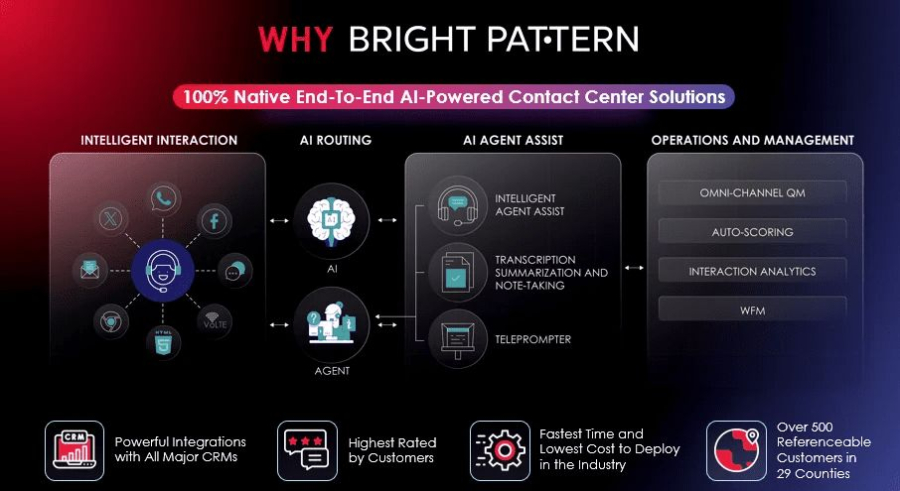
2. Genesys Cloud
A comprehensive AI-powered contact center platform offering omnichannel support, predictive routing, and automated agent assistance.
3. Five9
Cloud contact center solution with AI-driven workforce optimization and virtual agent capabilities for handling high-volume customer interactions.
4. NICE inContact CXone
Offers advanced analytics, AI-powered chatbots, and RPA integration to improve agent productivity and customer satisfaction.
5. Talkdesk
Cloud contact center platform with AI-driven insights, automated workflows, and personalized customer engagement features.
6. Zendesk
Customer service software with AI chatbots, automation tools, and multichannel support to streamline service delivery.
7. Avaya OneCloud
AI-enabled platform providing virtual assistants, analytics, and RPA integrations to enhance contact center operations.
8. Cisco Contact Center AI
Leverages AI and automation to provide predictive routing, virtual agents, and real-time agent assistance.
9. Aspect Via
Cloud-based platform combining AI chatbots, RPA, and omnichannel engagement to improve customer interactions.
10. HubSpot Service Hub
Customer service platform with AI-driven automation, chatbots, and analytics to improve engagement and streamline support.
What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automationuses software "bots" to mimic the actions a human takes on a computer. These bots follow clear, predefined rules to complete repetitive, structured tasks quickly and consistently.
Think of RPA as your digital assembly line worker: fast, reliable, and ideal for tasks that are the same every time.
Typical RPA capabilities
- Logging into applications and navigating interfaces
- Copying and pasting data between systems
- Filling out forms and updating records
- Extracting data from spreadsheets, PDFs, or emails (when structured)
- Triggering workflows based on simple rules or schedules
Key benefits of RPA
- Speed and throughput— Bots work around the clock without breaks, massively increasing task volume.
- Accuracy— Once configured correctly, bots follow the same steps every time, slashing manual errors.
- Cost efficiency— Automating routine work frees people to focus on higher value activities.
- Fast deployment— RPA usually sits on top of existing systems, so you can automate without replacing core platforms.
- Compliance and auditability— Every bot action can be logged, simplifying audits and regulatory reporting.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligencerefers to systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. Instead of following only fixed rules, AI can learn from data, detect patterns, adapt to new information, and make predictions or decisions.
If RPA is your digital assembly line worker, AI is your digital analyst: it recognizes, reasons, and improves over time.
Typical AI capabilities
- Machine learningfor predictions, scoring, and classification (for example, risk scores, lead scoring, or demand forecasting).
- Natural language processing (NLP)to understand and generate human language (for example, chatbots, email triage, or document understanding).
- Computer visionto interpret images or videos (for example, ID verification or invoice scanning with unstructured layouts).
- Generative AIto create content, draft responses, summarize documents, or assist with knowledge retrieval.
Key benefits of AI
- Adaptability— AI systems can improve over time as they are exposed to more data.
- Handling complexity— AI performs well where rules are not obvious or where there is uncertainty and variability.
- Deeper insights— AI can uncover patterns in data that humans may miss, leading to better decisions.
- Enhanced experiences— AI powers personalized recommendations, intelligent assistants, and smart self service.
- Scalable expertise— AI helps capture and scale knowledge that would otherwise remain in the heads of a few experts.
RPA vs AI: What Is the Difference?
RPA and AI both automate work, but they do it in different ways and shine in different situations.
| Aspect | RPA | AI |
| Core idea | Rule based task automation | Data driven intelligence and learning |
| Type of tasks | Repetitive, predictable, structured | Complex, variable, unstructured |
| Inputs | Well defined formats, clear rules | Text, images, audio, messy or incomplete data |
| Decision making | Follows predefined rules and workflows | Makes predictions or recommendations based on data patterns |
| Learning | Does not learn automatically; changes require reconfiguration | Learns and improves through training and feedback |
| Implementation speed | Typically fast for well understood processes | May require more time for data preparation and model training |
| Best suited for | High volume back office processes | Analysis, interpretation, prediction, and personalization |
In simple terms
- RPAis best when you knowexactlywhat needs to be done and the steps rarely change.
- AIis best when you need systems tofigure outwhat to do from data or context.
Where RPA Shines: Ideal Use Cases
RPA delivers quick, visible wins wherever there are clear rules and repetitive tasks. Typical high impact examples include:
1. Finance and accounting
- Automated invoice data entry when formats are consistent.
- Bank reconciliation and matching transactions across systems.
- Routine report generation and distribution.
2. HR and payroll
- Onboarding steps such as creating user accounts and provisioning access.
- Payroll calculations based on clear policies and time sheets.
- Updating employee records across multiple systems.
3. Operations and back office processing
- Order entry and confirmation when order formats follow a standard.
- Copying data between legacy systems with no direct integration.
- Status updates, notifications, and simple workflow routing.
In all of these, the primary benefits arespeed,accuracy, andcost savingswithout changing underlying systems.
Where AI Shines: Ideal Use Cases
AI thrives when tasks require understanding, judgment, or pattern recognition beyond simple rules.
1. Customer experience and support
- AI powered chatbots and virtual assistants that interpret natural language queries.
- Automatic email or ticket classification and routing based on content.
- Sentiment analysis to prioritize unhappy or at risk customers.
2. Document and knowledge intelligence
- Extracting key fields from complex or variable documents, such as invoices from different suppliers.
- Summarizing long reports or policies into short, actionable insights.
- Intelligent search across large knowledge bases using natural language questions.
3. Prediction and optimization
- Forecasting demand, sales, or staffing needs.
- Detecting suspicious behavior for fraud monitoring.
- Optimizing pricing, inventory, or routing based on historical patterns.
Here, the advantages arebetter decisions,personalized experiences, andscalable expertisethat gets smarter over time.
RPA vs AI: You Do Not Have to Choose Only One
The most powerful automation strategies treat RPA and AI as a team, not as competitors. RPA handles the repetitive clicks and data movement; AI handles the thinking, understanding, and predicting. Combined, they deliver end to end intelligent automation.
How RPA and AI complement each other
- AI as the brain, RPA as the hands— AI analyzes data and decides the best action; RPA executes it quickly across systems.
- RPA feeds AI— RPA can collect, clean, and prepare data from multiple systems, improving the quality of data available for AI models.
- AI enhances RPA— When rules would otherwise break, AI can interpret messy inputs (like free text or unstructured documents) so RPA can continue the process.
Example: Intelligent invoice processing
- AIreads varied invoice layouts, recognizes fields (supplier name, amount, due date), and validates values.
- RPAlogs into the finance system, posts the invoice, updates status, and triggers approvals.
The result is a highly automated, end to end flow that handles far more scenarios than RPA or AI alone.
Choosing RPA vs AI: A Practical Decision Guide
Instead of starting with technology, start with the process or problem. Then answer a few simple questions to decide which approach to lead with.
Question 1: How structured is the work?
- Highly structured(same steps every time, clear rules, consistent inputs) →RPA first.
- Unstructured or variable(free text, changing layouts, subjective decisions) →AI involved.
Question 2: Is the decision logic known in advance?
- If you can explain the logic as clear rules ("if X then Y"), RPA can usually handle it.
- If the decision depends on patterns in data, probabilities, or nuance, AI is a better fit.
Question 3: What is your timeline?
- Forquick winswith limited change, RPA projects can often be deployed faster.
- Forstrategic insightsand advanced capabilities, AI may take longer upfront but continues to add value as it learns.
Question 4: What resources do you have?
- RPAprimarily requires process knowledge, access to systems, and configuration skills.
- AIbenefits from access to quality data, domain experts, and the ability to experiment and refine models.
In many cases, the best approach is to start with RPA to stabilize and streamline processes, then layer AI where it delivers the most intelligence and flexibility.
Business Benefits: What You Can Expect from RPA and AI
Both RPA and AI directly support core business goals. When thoughtfully implemented, organizations often see benefits such as:
1. Productivity and capacity
- Bots and AI services run 24 / 7, dramatically increasing processing capacity without linearly increasing headcount.
- Teams spend less time on repetitive work and more time on creative, strategic, and relationship driven tasks.
2. Quality and consistency
- RPA reduces manual errors in data entry and process execution.
- AI applies consistent decision criteria across large volumes of cases.
3. Customer and employee experience
- Faster response times, more accurate information, and round the clock support.
- Employees can focus on problem solving, collaboration, and innovation instead of repetitive tasks.
4. Insight and agility
- AI generates insights from operational data that inform better decisions.
- RPA allows organizations to adapt processes quickly without waiting for major system changes.
Designing a Roadmap for RPA and AI
A clear roadmap helps you move from isolated pilots to scalable, high impact automation.
Step 1: Identify high value processes
- Look for high volume, repetitive tasks with measurable impact on cost, speed, or customer satisfaction.
- Map the steps, systems involved, and pain points.
Step 2: Classify opportunities as RPA first, AI first, or combined
- RPA first— Clear rules, structured data, quick wins.
- AI first— Need for interpretation, prediction, or personalization.
- Combined— End to end processes where some steps are structured and others are not.
Step 3: Start small, prove value, then scale
- Deliver a small, visible win within weeks to build momentum.
- Measure outcomes such as time saved, error reduction, and satisfaction improvements.
- Use those results to prioritize and fund the next wave of initiatives.
Step 4: Build the right foundation
- Establish clear ownership for automation and AI initiatives.
- Create standards for security, governance, and change management.
- Develop internal skills so teams can design, monitor, and continuously improve automations.
Common Myths About RPA and AI
Clarifying a few myths makes it easier to design the right strategy.
Myth 1: RPA will automatically become AI
RPA and AI are distinct technologies. You can add AI components (such as document understanding or chatbots) to an RPA workflow, but RPA itself remains rules based. The advantage is that you can combine them flexibly: use RPA where rules work, and plug in AI where intelligence is needed.
Myth 2: You must choose RPA or AI
In practice, mature organizations useboth. RPA maximizes efficiency in stable, repeatable tasks, while AI unlocks new capabilities in understanding, personalization, and prediction. Together, they form a powerful automation stack.
Myth 3: Automation only cuts costs
Cost savings are important, but they are only part of the story. Well designed RPA and AI projects also improve experience, enhance quality, and create capacity for innovation and growth. Many organizations reinvest the time saved into higher value work that directly supports revenue and customer loyalty.
Summary: RPA vs AI in One View
To recap the core ideas:
- RPAautomateshowwork is executed, following clear rules to handle repetitive, structured tasks quickly and reliably.
- AIaddsintelligenceto your workflows, interpreting data, making predictions, and adapting to change.
- Together, they enable intelligent automation that can transform efficiency, quality, and customer experience across the organization.
When you view RPA and AI as complementary, you can design solutions that combine the strengths of both: RPA for dependable execution, AI for smart decisions. That combination is where the biggest gains in productivity, insight, and competitive advantage are waiting.
